Let me tell you about the resistor color code, how it works, and Standard resistor values. We often look at a lot of resistors in many electronic circuits.
Do you know how to use it? How it works. I think it is a very important electronic device. If you do not have them. Your project may not work.
What is a resistor
The resistor is an electronics component. Meet Resistors in the image below.

It looks like a beautiful worm. With 2 legs on the head and end of the body. The 1/4 watts resistor is my most used shape.
And, Look at the symbol here.
What does a resistor do
It will resist or limit the current flowing it. The levels or size that they are resisting. We call the resistance.
If more resistance, less current flows in the circuit. You may not imagine. The current looks like the water in a pipe, below.
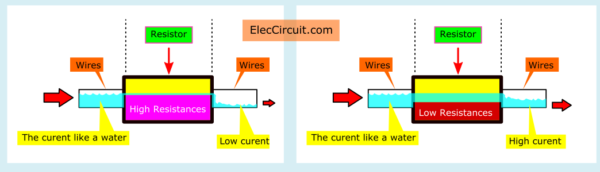
- The left resistor has high resistance. So the current can flow is low.
- But on the other hand, the right has low resistance inside. So the current can flow through it higher.
Many ways to use them
My daughter asked, “Why do you need a resistor?” The resistors will resist the flow of electricity. Also, we can use them a lot. For example,
- Using the resistor in a series circuit.
- They are very useful for reducing the current to the LED. Which it can damage with too much current.
- Most using resistors to divide a voltage into a smaller voltage.
- Resistors are used to increase the time required to charge capacitors and speed up the discharged of capacitors. Read: RC circuit time constant
- They are also used to control the gain of amplifiers.
Resistor color code
When we look at the resistor. We will notice many color bands on it. These colors show their resistance. We can measure them in ohms. When we write it, we can write an omega symbol, Ω.
1Ω is quite small so resistor values are often given in kΩ and MΩ.
For example,
1kΩ =1,000Ω
10kΩ = 10,000Ω
100kΩ = 100,000Ω
1MΩ =1,000,000Ω.
Why use color codes? As the resistors are small components. It can be difficult to see resistor values on them. So, these resistors have color-coded instead.
Resistor color code calculator
To begin with, look at the block diagram below. Now, most resistors have 4 color bands. It will have the same color for 0.25 watts, 0.5 watts, 1 watts, and 2 watts. When I was a young boy. I used to see the three color bands on AM receiver radio.
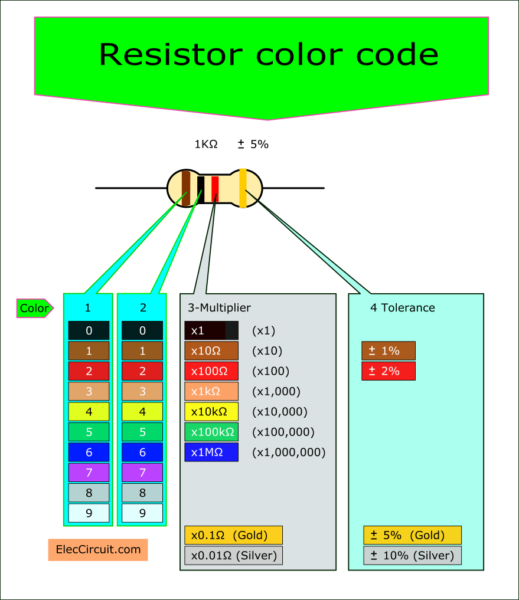
Suppose we have a resistor color code, brown, black, red, and gold. How much is its resistance?
Secondly, start to look at the color band from left to right. The first is the first digit of the resistance. We know the first band is “1” in resistance.
Then, the second band is the second digit. It is black for “0”.
Now, we have the resistance is 10.
Look at the third color band is red. The multiplier is 100Ω.
So, the resistance is 10 x 100Ω or 1kΩ
The fourth color band means an actual resistance, tolerance. It is gold, so its tolerance of ±5 percent, 25Ω.
Thus in real use, its resistance is between 950Ω and 1050Ω.
If you see the resistors having a tolerance resistance of 10%(silver). You can get it is the same this how.
Look at the resistor again. You will notice two group colors. First, tolerance is one band only, often for gold. Second, three bands are the resistance value.
How to read resistor color code without calculating
My son does not like to use how above. He finds an easier way.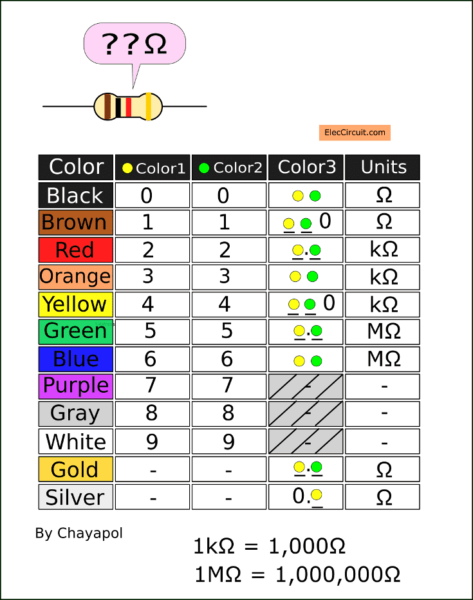
We can decode the resistor color without having to calculate with this table.
You may not understand how to use it. When more used more understand!
For example, You have 6 resistors. The last color band is Glod. So, it is a 5% tolerance. What is each resistance?
1. The first resistor,—Brown, Black, Red, and Gold. First, Brown and Black are 10. Second, look at the third color band is red. We put a dot between the first color and the second color band. It is 1.0. Then we put a kΩ as its unit. Now we have 1.0kΩ or 1kΩ.
2. The second resistor,—Yellow, Purple, Red, and Gold. First, yellow and purple are 47. Then, we put the dot between the first and second colors. It is 4.7. Next, we put the kΩ. So its resistance is 4.7kΩ.
3. Third resistor,—Orange, Orange, Orange, Gold. First, yellow and purple are 33. Then, we put a kΩ behind the second color as the unit. So its resistance is 33kΩ.
4. Fourth resistor,—Red, Red, Yellow, Gold. First, Red and Red are 22. Then, we put 0 (zero) behind the second color. It is 220. Next, put a kΩ behind the zero as the unit. So its resistance is 220kΩ.
5. Fifth resistor,—Brown, Black, Gold, Gold. First, Brown and Black are 10. When the third color band is Gold, we put the dot between the first color and second color band. It is 1.0 and the unit is Ω. So, the resistance is 1.0Ω or 1Ω.
6. Sixth resistor,—Green, Black, Silver, and Gold. First, Green and Black are 50. When the third color band is Silver, we put the dot font in the first color band. It is 0.50 and the unit is Ω. So, the resistance is 0.50Ω or 0.5Ω.
Standard resistor values table 5% tolerance
The following are the standard resistor values table available in carbon film with 5
percent tolerance.
| 1Ω | 10Ω | 100Ω |
| 1.1Ω | 11Ω | 110Ω |
| 1.2Ω | 12Ω | 120Ω |
| 1.3Ω | 13Ω | 130Ω |
| 1.5Ω | 15Ω | 150Ω |
| 1.6Ω | 16Ω | 160Ω |
| 1.8Ω | 18Ω | 180Ω |
| 2Ω | 20Ω | 200Ω |
| 2.2Ω | 22Ω | 220Ω |
| 2.4Ω | 24Ω | 240Ω |
| 2.7Ω | 27Ω | 270Ω |
| 3Ω | 30Ω | 300Ω |
| 3.3Ω | 33Ω | 330Ω |
| 3.6Ω | 36Ω | 360Ω |
| 3.9Ω | 39Ω | 390Ω |
| 4.3Ω | 43Ω | 430Ω |
| 4.7Ω | 47Ω | 470Ω |
| 5.1Ω | 51Ω | 510Ω |
| 5.6Ω | 56Ω | 560Ω |
| 6.2Ω | 62Ω | 620Ω |
| 6.8Ω | 68Ω | 680Ω |
| 7.5Ω | 75Ω | 750Ω |
| 8.2Ω | 82Ω | 820Ω |
| 9.1Ω | 91Ω | 910Ω |
| 1kΩ | 10kΩ | 100kΩ |
| 1.1kΩ | 11kΩ | 110kΩ |
| 1.2kΩ | 12kΩ | 120kΩ |
| 1.3kΩ | 13kΩ | 130kΩ |
| 1.5kΩ | 15kΩ | 150kΩ |
| 1.6kΩ | 16kΩ | 160kΩ |
| 1.8kΩ | 18kΩ | 180kΩ |
| 2kΩ | 20kΩ | 200kΩ |
| 2.2kΩ | 22kΩ | 220kΩ |
| 2.4kΩ | 24kΩ | 240kΩ |
| 2.7kΩ | 27kΩ | 270kΩ |
| 3kΩ | 30kΩ | 300kΩ |
| 3.3kΩ | 33kΩ | 330kΩ |
| 3.6kΩ | 36kΩ | 360kΩ |
| 3.9kΩ | 39kΩ | 390kΩ |
| 4.3kΩ | 43kΩ | 430kΩ |
| 4.7kΩ | 47kΩ | 470kΩ |
| 5.1kΩ | 51kΩ | 510kΩ |
| 5.6kΩ | 56kΩ | 560kΩ |
| 6.2kΩ | 62kΩ | 620kΩ |
| 6.8kΩ | 68kΩ | 680kΩ |
| 7.5kΩ | 75kΩ | 750kΩ |
| 8.2kΩ | 82kΩ | 820kΩ |
| 9.1kΩ | 91kΩ | 910kΩ |
| 1MΩ | 3MΩ | 9.1MΩ |
| 1.1MΩ | 3.3MΩ | 10MΩ |
| 1.2MΩ | 3.6MΩ | 12MΩ |
| 1.3MΩ | 3.9MΩ | 13MΩ |
| 1.5MΩ | 4.3MΩ | 15MΩ |
| 1.6MΩ | 5.1MΩ | 16MΩ |
| 1.8MΩ | 5.6MΩ | 18MΩ |
| 2MΩ | 6.2MΩ | 20MΩ |
| 2.2MΩ | 6.8MΩ | 22MΩ |
| 2.4MΩ | 7.5MΩ | |
| 2.7MΩ | 8.2MΩ | |
| 0.5Ω | 0.22Ω | 0Ω |
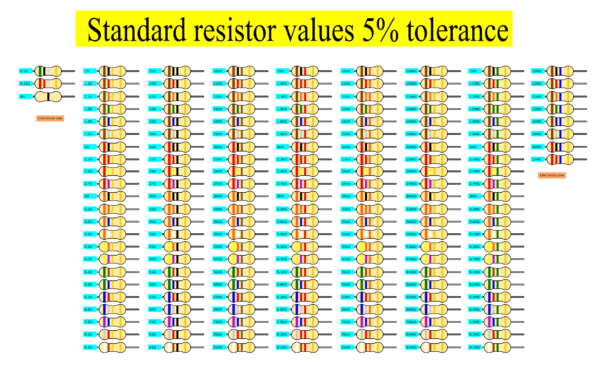
OR you can look list of color codes on each resistor here.
What is more? Sometimes you cannot find a resistor. You may use this way to do it.
DIY Cheap Resistance Decade Circuit
Here is a DIY resistance decade tool for testing and calibration. Because it can substitute into a circuit with all standard values. This ideal is the cheapest that uses resistors and wires only.
In each experiment, a resistor needs to involve at all times and is often unable to find the required resistance. This problem will solve with the “DIY Cheap Resistance Decade Circuit”.
How it works
This variable resistor is not “the normal potentiometer”. It is a very high accuracy and tolerates low current. We need a “decade resistor” in the image below.
The way it works is very simple, is organized as a series resistor. The first set resistors have four resistors include with 1, 2, 3 and 6 ohms. The set 2 and 3 to series will add value up 10 times and 100 times is 10, 20, 30, 60, 100, 200, 300, 600 in sequence. As shown in Figure 2

How to application
For example, resistance is 39 ohms. Use copper alligator clips to connect the resistors 3, 6, and 30 ohms in series as Figure 2. And If you Require the resistances as a decimal fraction. Such as the 5.2 ohms. But we have 2.2 ohms resistors. Just connects in series with the 3 ohms resistors only.
The advantage of this decade’s resistors is cheap. Selecting the desired setting is simple and accurate. Without using the meter to adjust the resistance. Tolerate high current (Depending on the power tolerate rate that you’re using). The disadvantage is the Wasted space If the installation is not good, it makes the resistor shorted together.
GET UPDATE VIA EMAIL
I always try to make Electronics Learning Easy.
Related Posts

I love electronics. I have been learning about them through creating simple electronic circuits or small projects. And now I am also having my children do the same. Nevertheless, I hope you found the experiences we shared on this site useful and fulfilling.


Thanks.
I have to thank you for your blog.as I am getting older and have very little education your article on lm317has made it simple to understand
Much respect to you sincerely
Lamont
Hi Lamont,
I am always happy. When the elderly said Interested in learning electronics. It makes our lives useful. Time passed quickly and everyone enjoyed. Also, the children liked it.
I will dedicate to writing the easiest readable articles.
It is good teaching! so easy to learn. Keep your job!
Thanks for your feedback.
I came across your article and learned something new today. Easy to understand, thank you!
Hello Meera,
Thanks for your feedback.