My students (children) ask me what the difference is between analog and digital. It is a good question. But how can we answer him clearly and simply? We have heard both words, such as in terms of audio or video being transformed into electrical signals.
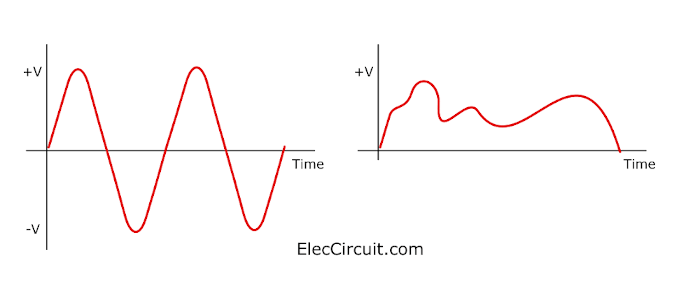
In short, the technology of analog information is just a signal that has a wide range of amplitude. And It has to be smooth and continuous.
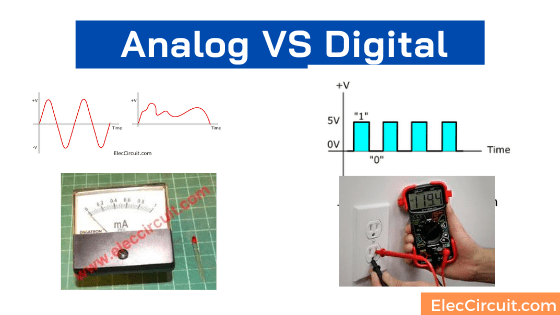
But in the digital on the other hand, information is summed into one and zero formats. We called it “a binary”. Each bit has two distinct amplitudes.
Are you a beginner? Learn Basic Electronics
What is an Analog Signal?
It is continuous data that has a varying signal amplitude. The change in signal is gradual and curved. The change in value (Y-axis) co-evolved with the increase in time (X-axis).
We will see this type of signal all around us, both man-made and natural. For example, sound, light, wind, heat, etc.
Does it seem clearer to you now?
In electronics alone, there are a lot of analog signals. Such as the output or input from an LDR (light sensor), Microphone, Speaker, Radio, etc.
A power amplifier
Another example of an analog system is the power amplifier. It will produce an output voltage of any value within the range of its power supply.
Analog meter
It can measure and display any value within the range available on the scale. However, accuracy is limited by our ability to read.
Shown below is a type of analog meter called a 0-1mA galvanometer.

Learn: How to use an analog meter
Like if the meter reads 0.3mA. Its needle is pointed about halfway between 0.2mA and 0.4mA. We cannot accurately read a smaller value than the one being labeled.
Noise in Analog circuits
All electronic circuits suffer from noise interference signals. This is an unwanted signal mixed in with the desired signal.
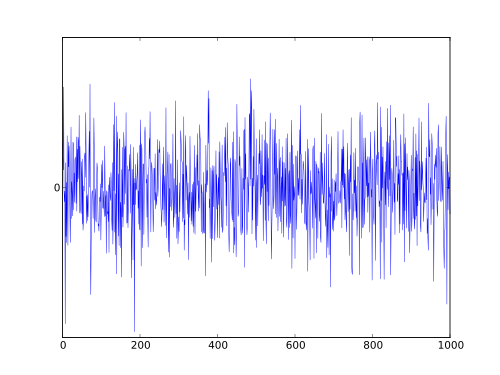
For example, an amplifier can pick up and hum from an AC main (50Hz AC main). It is difficult to eliminate the noise from the Analog signal. Because it is difficult to distinguish between interference and the desired signal.
Pros of Analog Signals
- Easier, needs fewer components, and is cheaper.
- More suitable for sending and receiving audio and video signals.
- Gives more natural audio signals.
- Higher quality and smoothness for audio signals.
- Better data resolution.
- Gives a signal with a lower bandwidth.
Cons of Analog Signals
- Lower general signal quality.
- High rate of noise interference.
- High signal loss.
- Needs higher-quality cables, which cost more.
- Records of audio and video have a large size and use more power.
- Equipment and recording tape can deteriorate quickly when used for a while.
- Harder to edit or transform signals.
- Recorders and readers for those signals are expensive and hard to get hold of these days.
- Hards to synchronize the signal.
- Low compatibility across devices.
What is Digital Signal?
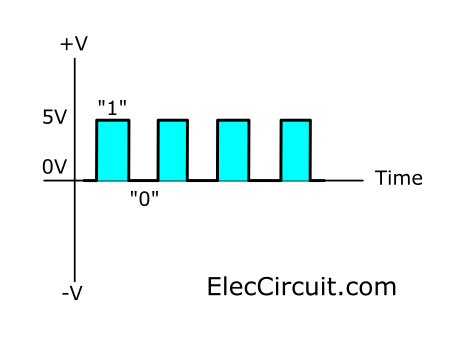
The signals are associated with Discrete Data. Have a certain size. They may jump between two values: the highest signal and the lowest signal.
Or discrete steps like either 0V or 5V. Timing graphs of these signals look like square waves. Or we called Logic states.
Look at the square wave signal
Digital systems are made up of devices such as logic gates, flip-flops, shift registers, and counters. Computers are an example of digital systems.
Today we prefer to use a Microcontroller like Arduino to replace a normal analog.
What is more?
Digital Meter
An example of a digital circuit closest to us is a digital multimeter. We can use it to read many values and have higher accuracy than an analog meter.

Credit: Photo Equus
Not only that I want to explain to you about this, too
LEARN: Relationship Between Current and Voltage
Logic states
Most digital systems use a simple signal type. Which has only two values This type of signal is called the logic signal. Because these two values (or status) can be called “true” and “false”. Normally the positive power supply voltage is + Vs instead of true, and 0V represents false.
Obvious advantages of a digital signal, we can get rid of the interference signal easily. It is convenient to distinguish the desired signal. Which it has a specific value.
For example, If the logic signal means + 5V (True) or 0V (False) .. noise is as high as 2.5V. We can cut it out. We can isolate all voltages above 2.5V, is True and the voltage less than 2.5V are False.
Pros of Digital Signals
- Digital data can be easily compressed.
- Any information in the digital form can be encrypted.
- Equipment that uses digital signals is more common and less expensive.
- Digital signal makes running instruments free from observation errors like parallax and approximation errors.
- A lot of editing tools are available
- You can edit the sound without altering the original copy
- Easy to transmit the data over networks
Cons of Digital Signals
- Sampling may cause a loss of information.
- A/D and D/A demand mixed-signal hardware
- Processor speed is limited
- Develop quantization and round-off errors
- It requires greater bandwidth
- Systems and processing is more complex.
Difference Between Analog and Digital
By the way, let’s compare them.
| Analog | Digital | |
| Signal | Continuous signal | time separated signals |
| Waves | sine waves | square waves |
| Errors | Analog instruments usually have a scale that is cramped at the lower end and give considerable observational errors. | Digital instruments are free from observational errors like parallax and approximation errors. |
| Impedance | Low | High order of 100 Megaohm |
Sure, this may be quite full but I want to see you improve your skills. So, I recommend:
Sparkfun.com, Diffen.com, Guru99.com
GET UPDATE VIA EMAIL
I always try to make Electronics Learning Easy.

I love electronics. I have been learning about them through creating simple electronic circuits or small projects. And now I am also having my children do the same. Nevertheless, I hope you found the experiences we shared on this site useful and fulfilling.